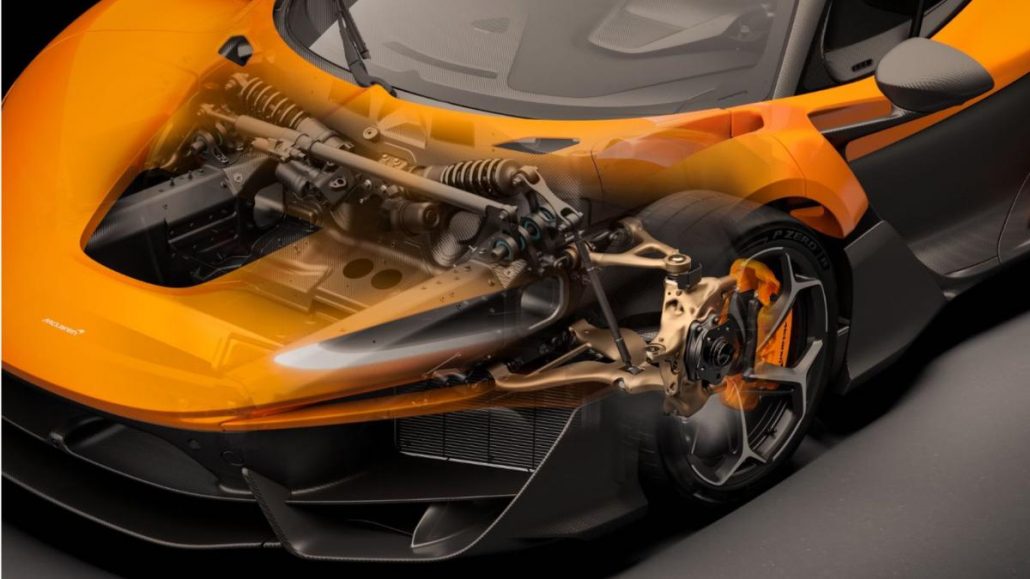

McLaren Automotive has revealed that it used Divergent Technologies’ cutting-edge 3D printing technology to design and manufacture the suspension components for its highly anticipated W1 supercar. This collaboration marks a significant step in McLaren’s continued push to integrate digital manufacturing into high-performance automotive engineering.
Collaborative Development of Advanced Suspension Hardware
The partnership with Divergent allowed McLaren engineers to create complex suspension structures for the W1 supercar, including the front upper wishbone, aero form lower wishbone, and front upright. These components were 3D printed using Divergent’s Adaptive Production System (DAPS), a digital manufacturing process that enables rapid prototyping and high precision for automotive applications. This collaboration follows an earlier announcement of a multi-year partnership to use Divergent’s DAPS technology for producing chassis components in McLaren’s next-generation vehicles.
Formula 1-Inspired Suspension for McLaren W1
The W1 supercar boasts a Formula 1-inspired front suspension, integrated directly into the car’s Aerocell carbon fiber monocoque. By using 3D printing, McLaren was able to optimize the design of the suspension components for increased durability and stiffness, while also enabling quicker design iterations. The use of this technology has allowed McLaren to create lighter, more efficient suspension systems that enhance the overall driving experience and performance of the W1.
Divergent’s Technology Revolutionizing Automotive Manufacturing
Divergent Technologies’ DAPS system has proven transformative in the automotive industry. In addition to McLaren, the system has been used by Aston Martin to 3D print a rear subframe for its DBR22 concept vehicle, and by General Atomics Aeronautical Systems for optimizing designs for unmanned aerial systems (UAS). McLaren Racing, McLaren’s Formula 1 team, has also utilized 3D printing technology, producing 9,000 parts annually using Stratasys stereolithography machines.
A New Era of Digital Manufacturing in Supercars
The integration of 3D printing into McLaren’s manufacturing processes is part of a larger trend of using advanced digital technologies to push the limits of performance and innovation in high-end automotive engineering. As McLaren continues to explore the potential of additive manufacturing, it aims to create even more efficient, lightweight, and high-performing vehicles in the future.






Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.